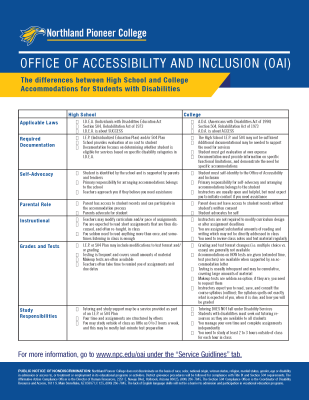
What is the Difference Between High School and College?
Applicable Laws
High School
- I.D.E.A (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act) is about success
- Section 504, Rehabilitation Act of 1973
College
- A.D.A. (Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990) is about access
- Section 504, Rehabilitation Act of 1973
Self-Advocacy
High School
- Student is identified by the school and is supported by parents and teachers
- Primary responsibility for arranging accommodations belongs to the school
- Teachers approach you if they believe you need assistance
College
- Student must self-identify to the Office of Accessibility and Inclusion
- Primary responsibility for self-advocacy and arranging accommodations belongs to the student
- Students will need to advocate for their needs and seek out available campus resources
Documentation
High School
- I.E.P. (Individualized Education Plan) and/or 504 Plan)
- School may assist with testing and screening for determining eligibility
- Documentation focuses on determining eligibility for services based on disabilities as specified by the I.D.E.A.
College
- A High School I.E.P. and Section 504 Plan may provide sufficient information for determining reasonable accommodations
- Documentation from a healthcare provider may be requested to support the provision of accommodations
Notification of Accommodation
High School
- In high school, accommodations are written on an "Individualized Education Plan (IEP)" or "504 Plan"
College
- At NPC, accommodations are written on an "Accommodation Notification Letter"
Parental Role
High School
- Parent has access to student records and can participate in the accommodation process
- Parent advocates for student
College
- Parent does not instantly have access to student records
- Student is responsible for advocating for self
Academic
High School
- Teachers may modify curriculum
- I.E.P. or 504 plan may include modifications to test format and/or grading
- Tutoring and study support may be a service provided as part of an I.E.P. or 504 plan
- Students' time and assignments are structured by others
- Teachers often take time to remind students of assignments and due dates
- Students may study outside of class as little as 0 to 2 hours a week, and this may be mostly last-minute test preparation
College
- Professors are not required to modify curriculum
- Accommodations for tests (ex: extended time, etc.) are appropriate academic adjustments granted through the accommodations process
- Tutoring does not fall under The Office of Accessibility and Inclusion. Students are encouraged to seek out tutoring resources available to all students, here is a link to those services: Tutoring | Northland Pioneer College, Arizona (npc.edu)
- Students manage their own time and complete assignments independently
- College students are expected to read, save, and consult the course syllabus, which outlines what is expected, when it is due, and how it will be graded
- It is recommended that students’ study at least 2-3 hours per credit hour (i.e., 6-9 hours of study for a 3-credit hour course)
Last Updated 6/11/2024.
Modified from West Chester University Office of Services for Students with Disabilities and University of California Santa Barbara. Adapted from AHEAD Guidelines